5. Creating a new classifier in CapyMOA#
In this tutorial we show how simple it is to create a new learner in CapyMOA using Python.
We choose to make an implementation of the canonical ensemble classifier Online Bagging (AKA OzaBag).
The base learner is a CapyMOA object, which allows us to use either sklearn or MOA algorithms; so even though it will be all implemented in Python by us, it can be quite efficient in terms of run time as it depends on the base learner.
Reference: Online bagging and boosting. Oza, Nikunj C., and Stuart J. Russell. In International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp. 229-236. PMLR, 2001.
More information about CapyMOA can be found at https://www.capymoa.org.
last update on 04/12/2025
5.1 Creating the classifier#
The first step is to extend the
Classifierabstract class fromcapymoa.baseand implement the required methods:__init__(self, schema=None, random_seed=1, ...)train(self, instance)predict(self, instance)predict_proba(self, instance)
There is no need to pay much attention to the auxiliary function
poisson, even though it is a defining characteristic of Online Bagging algorithm but not that relevant for our example.We specify the parameter
base_learner_classas a class identifier and proceed to instantiate it inside the__init__method:
self.ensemble = []
for i in range(self.ensemble_size):
self.ensemble.append(self.base_learner_class(schema=self.schema))
[2]:
from capymoa.base import Classifier
from capymoa.classifier import HoeffdingTree
from collections import Counter
import numpy as np
# Online Bagging Implementation
class CustomOnlineBagging(Classifier):
def __init__(
self, schema=None, random_seed=1, ensemble_size=5, base_learner_class=None
):
super().__init__(schema=schema, random_seed=random_seed)
self.ensemble_size = ensemble_size
self.base_learner_class = base_learner_class
if self.base_learner_class is None:
self.base_learner_class = HoeffdingTree
self.ensemble = []
for _ in range(self.ensemble_size):
self.ensemble.append(self.base_learner_class(schema=self.schema))
def __str__(self):
return "CustomOnlineBagging"
def train(self, instance):
for i in range(self.ensemble_size):
for _ in range(np.random.poisson(1.0)):
self.ensemble[i].train(instance)
def predict(self, instance):
predictions = []
for i in range(self.ensemble_size):
predictions.append(self.ensemble[i].predict(instance))
majority_vote = Counter(predictions)
prediction = majority_vote.most_common(1)[0][0]
return prediction
def predict_proba(self, instance):
probabilities = []
for i in range(self.ensemble_size):
classifier_proba = self.ensemble[i].predict_proba(instance)
classifier_proba = classifier_proba / np.sum(classifier_proba)
probabilities.append(classifier_proba)
avg_proba = np.mean(probabilities, axis=0)
return avg_proba
5.2 Evaluating the classifier#
We use the same approach as when we evaluate any other CapyMOA learner.
We show how it is simple to use learners with different backends in our implementation, e.g.,
HoeffdingTree(MOA)SGDClassifier(sklearn)
[3]:
from capymoa.evaluation import prequential_evaluation
from capymoa.evaluation.visualization import plot_windowed_results
from capymoa.datasets import Electricity
from capymoa.classifier import SGDClassifier
elec_stream = Electricity()
# Creating a learner: using a hoeffding adaptive tree as the base learner
ob_ht = CustomOnlineBagging(
schema=elec_stream.get_schema(), ensemble_size=5, base_learner_class=HoeffdingTree
)
ob_sgd = CustomOnlineBagging(
schema=elec_stream.get_schema(), ensemble_size=5, base_learner_class=SGDClassifier
)
results_ob_ht = prequential_evaluation(
stream=elec_stream, learner=ob_ht, window_size=4500
)
print(
f"CustomOnlineBagging(HT) accuracy: {results_ob_ht.cumulative.accuracy()}, wallclock: {results_ob_ht.wallclock()}"
)
results_ob_sgd = prequential_evaluation(
stream=elec_stream, learner=ob_ht, window_size=4500
)
print(
f"CustomOnlineBagging(SGD) accuracy: {results_ob_sgd.cumulative.accuracy()}, wallclock: {results_ob_sgd.wallclock()}"
)
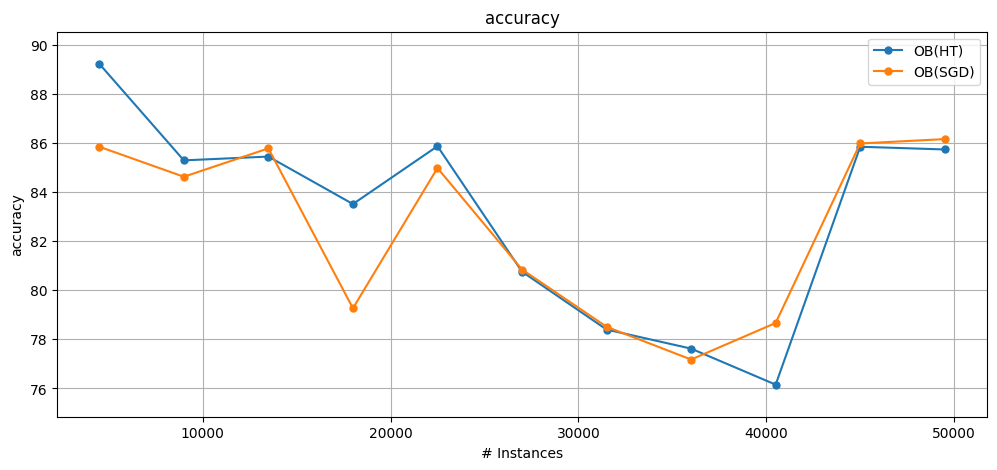
results_ob_ht.learner = "OB(HT)"
results_ob_sgd.learner = "OB(SGD)"
plot_windowed_results(results_ob_ht, results_ob_sgd, metric="accuracy")
CustomOnlineBagging(HT) accuracy: 82.52339336158192, wallclock: 4.913214683532715
CustomOnlineBagging(SGD) accuracy: 82.4461511299435, wallclock: 4.222089529037476
5.3 CustomOnlineBagging and OnlineBagging#
Testing and training our custom online bagging implementation alongside the online bagging implementation from
capymoa.classifier.OnlineBagging.
[4]:
%%time
from capymoa.classifier import OnlineBagging
from capymoa.evaluation import ClassificationEvaluator
from capymoa.datasets import RBFm_100k
RBFm_100k_stream = RBFm_100k()
# Creating a learner without specifying the base_learner thus HoeffdingTree is used
custom_ob = CustomOnlineBagging(schema=RBFm_100k_stream.get_schema(), ensemble_size=5)
capy_ob = OnlineBagging(schema=RBFm_100k_stream.get_schema(), ensemble_size=5)
custom_ob_evaluator = ClassificationEvaluator(schema=RBFm_100k_stream.get_schema())
capy_ob_evaluator = ClassificationEvaluator(schema=RBFm_100k_stream.get_schema())
while RBFm_100k_stream.has_more_instances():
instance = RBFm_100k_stream.next_instance()
prediction_new = custom_ob.predict(instance)
prediction = capy_ob.predict(instance)
custom_ob_evaluator.update(instance.y_index, prediction_new)
capy_ob_evaluator.update(instance.y_index, prediction)
custom_ob.train(instance)
capy_ob.train(instance)
print(f"[custom] Online Bagging acc: {custom_ob_evaluator.accuracy()}")
print(f"[capymoa] Online Bagging acc: {capy_ob_evaluator.accuracy()}")
[custom] Online Bagging acc: 67.42899999999999
[capymoa] Online Bagging acc: 60.357000000000006
CPU times: user 15.4 s, sys: 42.7 ms, total: 15.5 s
Wall time: 14.1 s
[ ]: