Drift Detection in CapyMOA#
In this tutorial, we show how to conduct drift detection using CapyMOA.
Usage example of several detectors.
Example using ADWIN.
Evaluating detectors based on known drift locations.
Multivariate drift detection using ABCD.
More information about CapyMOA can be found at https://www.capymoa.org.
last update on 28/11/2025
[1]:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import capymoa.drift.detectors as detectors
1. Basic example#
Creating dummy data
[2]:
data_stream = np.random.randint(2, size=2000)
for i in range(999, 2000):
data_stream[i] = np.random.randint(6, high=12)
Basic drift detection example
[3]:
all_detectors = detectors.__all__
n_detections = {k: 0 for k in all_detectors}
for detector_name in all_detectors:
if detector_name == "STUDD":
continue
detector = getattr(detectors, detector_name)()
for i in range(2000):
detector.add_element(float(data_stream[i]))
if detector.detected_change():
n_detections[detector_name] += 1
print(pd.Series(n_detections))
ABCD 1
ADWIN 1
CUSUM 2
DDM 1
EWMAChart 1
GeometricMovingAverage 1
HDDMAverage 135
HDDMWeighted 88
OPTWIN 1
PageHinkley 2
RDDM 1
SEED 2
STEPD 1
STUDD 0
dtype: int64
2. Example using ADWIN#
[4]:
# detector = ADWIN(delta=0.001)
for i in range(2000):
detector.add_element(data_stream[i])
if detector.detected_change():
print(
"Change detected in data: " + str(data_stream[i]) + " - at index: " + str(i)
)
[5]:
# Detection indices
detector.detection_index
[5]:
[1000]
[6]:
# Warning indices
detector.warning_index
[6]:
[92,
521,
522,
523,
524,
525,
526,
527,
528,
533,
534,
535,
536,
537,
538,
539,
540,
541,
542,
543,
544,
638,
639,
640,
641,
644,
726,
729,
730,
731]
[7]:
# Instance counter
detector.idx
[7]:
4000
3. Evaluating drift detectors#
Assuming the drift locations are known, you can evaluate detectors using EvaluateDetector class.
This class takes a parameter called max_delay, which is the maximum number of instances for which we consider a detector to have detected a change. After max_delay instances, we assume that the change is obvious and has been missed by the detector.
[8]:
from capymoa.drift.eval_detector import EvaluateDriftDetector
drift_eval = EvaluateDriftDetector(max_delay=200)
The EvaluateDetector class takes two arguments for evaluating detectors:
The locations of the drift
The locations of the detections
[9]:
trues = np.array([1000])
preds = detector.detection_index
drift_eval.calc_performance(trues, preds, tot_n_instances=detector.idx)
[9]:
DriftDetectionMetrics(fp=0, tp=1, fn=0, precision=1.0, recall=1.0, episode_recall=1.0, f1=1.0, mdt=np.float64(0.0), far=0.0, ar=0.25, n_episodes=1, n_alarms=1)
4. Multivariate drift detection#
[10]:
from capymoa.drift.detectors import ABCD
from capymoa.datasets import ElectricityTiny
detector = ABCD()
## Opening a file as a stream
stream = ElectricityTiny()
[11]:
i = 0
loss_values = []
while stream.has_more_instances() and i < 5000:
i += 1
instance = stream.next_instance()
detector.add_element(instance)
loss_values.append(detector.loss())
if detector.detected_change():
print("Change detected at index: " + str(i))
Change detected at index: 2776
[12]:
detector = ABCD(model_id="pca")
## Opening a file as a stream
stream_change = np.hstack(
[np.random.uniform(0, 0.5, 3000), np.random.uniform(0.5, 1.0, 3000)]
)
stream_nochange = np.random.uniform(0, 1.0, len(stream_change))
stream = np.vstack([stream_change, stream_nochange]).T
print(f"A {stream.shape[-1]}-dimensional stream")
A 2-dimensional stream
[13]:
i = 0
loss_values = []
while i < len(stream):
instance = stream[i]
i += 1
detector.add_element(instance)
loss_values.append(detector.loss())
if detector.detected_change():
print("Change detected at index: " + str(i))
Change detected at index: 3060
[14]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(pd.Series(loss_values).rolling(10).mean())
plt.title("ABCD with PCA")
plt.xlabel("# Instances")
plt.ylabel("Reconstruction loss")
[14]:
Text(0, 0.5, 'Reconstruction loss')
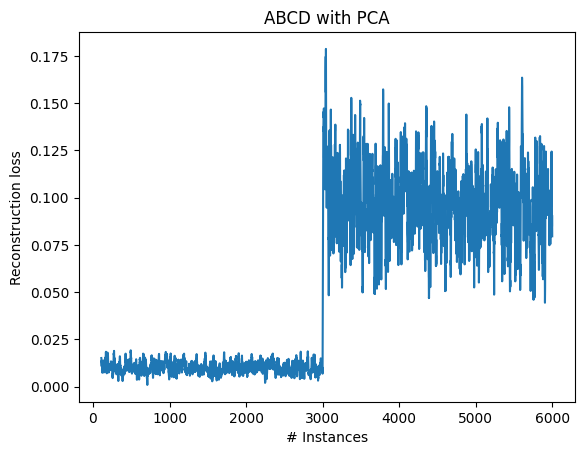
We see that a value of 1 as maximum reconstruction error is very conservative. By decreasing the maximum_absolute_value parameter, we can make change detection faster as it makes the applied statistical test more sensitive.
[15]:
detector = ABCD(model_id="pca", maximum_absolute_value=0.3)
i = 0
loss_values = []
while i < len(stream):
instance = stream[i]
i += 1
detector.add_element(instance)
loss_values.append(detector.loss())
if detector.detected_change():
print("Change detected at index: " + str(i))
Change detected at index: 3023