9. Automated machine learning#
This notebook contains some basics for autoML using CapyMOA:
Implement a custom model selection procedure using CapyMOA.
Perform hyperparameter optimisation, and model selection using CapyMOA’s AutoML features.
More information about CapyMOA can be found at https://www.capymoa.org.
last updated on 28/11/2025
[2]:
import contextlib
import io
from capymoa.datasets import Electricity
from capymoa.evaluation import prequential_evaluation
from moa.streams import ConceptDriftStream
from capymoa.stream.drift import DriftStream, AbruptDrift, GradualDrift
from capymoa.evaluation.visualization import plot_windowed_results
from capymoa.classifier import (
HoeffdingTree,
HoeffdingAdaptiveTree,
KNN,
NaiveBayes,
AdaptiveRandomForestClassifier,
StreamingRandomPatches,
LeveragingBagging,
)
from capymoa.stream.generator import SEA
from capymoa.automl import (
AutoClass,
BanditClassifier,
SuccessiveHalvingClassifier,
EpsilonGreedy,
)
# Setup the data streams for our experiments:
stream = Electricity()
drift_stream = DriftStream(
moa_stream=ConceptDriftStream(),
CLI="""
-s (generators.AgrawalGenerator -f 1)
-d (ConceptDriftStream
-s (generators.AgrawalGenerator -f 2)
-d (ConceptDriftStream -s (generators.AgrawalGenerator -f 3)
-d (generators.AgrawalGenerator -f 4) -p 30000 -w 0)
-p 20000 -w 0)
-p 10000
-w 0
""",
)
[3]:
def print_summary(label: str, results):
print(
f"{label.ljust(10)} Cumulative accuracy = {results.accuracy():.2f}, "
f"wall-clock time: {results.wallclock():.3f}"
)
9.1 Custom model selection#
In this section we manually define a method to select the best model based on its accuracy on a given stream. First we define a list of models to be tried and then we iterate over the stream to train and evaluate each model. The model with the highest accuracy is selected as the best model.
[4]:
# Define a generic adaptive learning function
def stream_learning_model_selection(model_list, window_size, max_instances):
best_accuracy = 0 # The best accuracy score
all_results = {}
for model in model_list:
results = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=model,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
all_results[model] = results
if results.cumulative.accuracy() > best_accuracy:
best_accuracy = results.cumulative.accuracy()
model_b = model
print_summary(f"Best ({model_b})", all_results[model_b])
return all_results
[5]:
# Code to select the best performing model
schema = stream.get_schema()
ht = HoeffdingTree(schema)
knn = KNN(schema)
arf = AdaptiveRandomForestClassifier(schema, ensemble_size=5)
srp = StreamingRandomPatches(schema, ensemble_size=5)
nb = NaiveBayes(schema)
model_list = [ht, knn, arf, srp, nb]
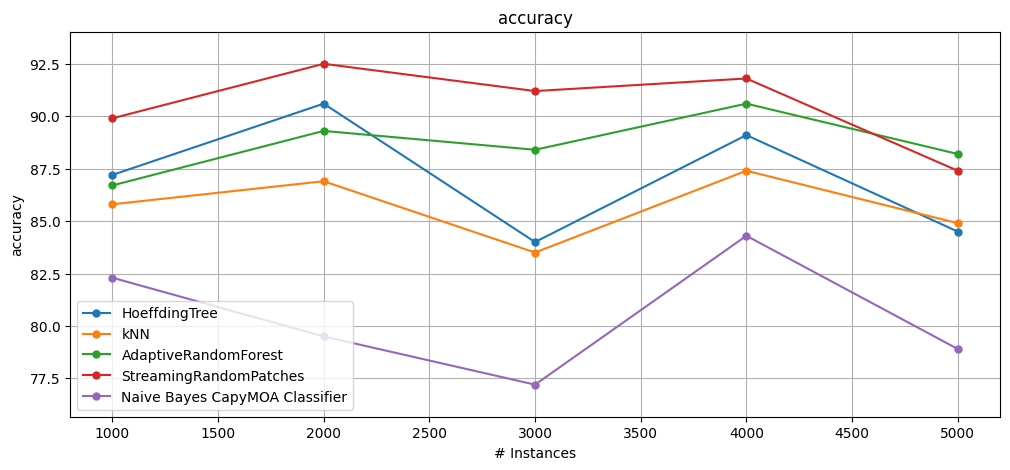
all_res = stream_learning_model_selection(model_list, 1000, 5000)
plot_windowed_results(*all_res.values(), metric="accuracy")
Best (StreamingRandomPatches) Cumulative accuracy = 90.56, wall-clock time: 2.070
9.2 AutoML#
The following example shows how to use the AutoClass algorithm using CapyMOA.
base_classifiersis a list of classifier class types that will be candidates for the AutoML algorithm. The AutoML algorithm will select the best classifier based on its performance on the stream.configuration_jsonis a json file that contains the configuration for the AutoML algorithm. An example of the configuration file is shown below:
Maroua Bahri, Nikolaos Georgantas. Autoclass: Automl for data stream classification. In BigData, IEEE, 2023. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10386362
[6]:
with open("./settings_autoclass.json", "r") as f:
settings = f.read()
print(settings)
{
"windowSize" : 1000,
"ensembleSize" : 10,
"newConfigurations" : 10,
"keepCurrentModel" : true,
"lambda" : 0.05,
"preventAlgorithmDeath" : true,
"keepGlobalIncumbent" : true,
"keepAlgorithmIncumbents" : true,
"keepInitialConfigurations" : true,
"useTestEnsemble" : true,
"resetProbability" : 0.01,
"numberOfCores" : 1,
"performanceMeasureMaximisation": true,
"algorithms": [
{
"algorithm": "moa.classifiers.lazy.kNN",
"parameters": [
{"parameter": "k", "type":"integer", "value":10, "range":[2,30]}
]
}
,
{
"algorithm": "moa.classifiers.trees.HoeffdingTree",
"parameters": [
{"parameter": "g", "type":"integer", "value":200, "range":[10, 200]},
{"parameter": "c", "type":"float", "value":0.01, "range":[0, 1]}
]
}
,
{
"algorithm": "moa.classifiers.lazy.kNNwithPAWandADWIN",
"parameters": [
{"parameter": "k", "type":"integer", "value":10, "range":[2,30]}
]
}
,
{
"algorithm": "moa.classifiers.trees.HoeffdingAdaptiveTree",
"parameters": [
{"parameter": "g", "type":"integer", "value":200, "range":[10, 200]},
{"parameter": "c", "type":"float", "value":0.01, "range":[0, 1]}
]
}
]
}
[7]:
max_instances = 20000
window_size = 2500
schema = stream.get_schema()
autoclass = AutoClass(
schema=schema,
configuration_json="./settings_autoclass.json",
base_classifiers=[KNN, HoeffdingAdaptiveTree, HoeffdingTree],
)
results_autoclass = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=autoclass,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
print_summary("AutoClass", results_autoclass)
AutoClass Cumulative accuracy = 88.33, wall-clock time: 53.758
We compare the performance of the AutoML algorithm against basic classifiers:
[8]:
ht = HoeffdingTree(schema)
hat = HoeffdingAdaptiveTree(schema)
knn = KNN(schema)
nb = NaiveBayes(schema)
results_ht = prequential_evaluation(
stream, ht, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances
)
results_hat = prequential_evaluation(
stream, hat, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances
)
results_knn = prequential_evaluation(
stream, knn, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances
)
results_nb = prequential_evaluation(
stream, nb, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances
)
print_summary("HT", results_ht)
print_summary("HAT", results_hat)
print_summary("KNN", results_knn)
print_summary("NB", results_nb)
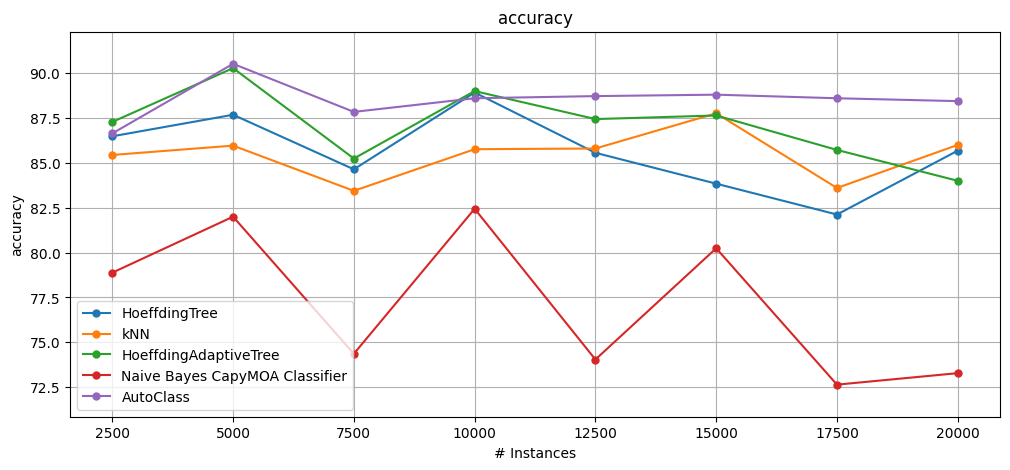
plot_windowed_results(
results_ht,
results_knn,
results_hat,
results_nb,
results_autoclass,
metric="accuracy",
)
HT Cumulative accuracy = 85.61, wall-clock time: 0.142
HAT Cumulative accuracy = 87.08, wall-clock time: 0.187
KNN Cumulative accuracy = 85.47, wall-clock time: 1.646
NB Cumulative accuracy = 77.23, wall-clock time: 0.071
9.3 AutoML with concept drift#
We test the same algorithms on a data stream with simulated concept drift:
[9]:
from capymoa.evaluation import prequential_evaluation
from capymoa.automl import AutoClass
max_instances = 40000
window_size = 4000
ht = HoeffdingTree(schema=drift_stream.get_schema())
hat = HoeffdingAdaptiveTree(schema=drift_stream.get_schema())
knn = KNN(schema=drift_stream.get_schema())
nb = NaiveBayes(schema=drift_stream.get_schema())
autoclass = AutoClass(
schema=drift_stream.get_schema(),
configuration_json="./settings_autoclass.json",
base_classifiers=[KNN, HoeffdingAdaptiveTree, HoeffdingTree],
)
results_ht = prequential_evaluation(
drift_stream, ht, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances
)
results_hat = prequential_evaluation(
drift_stream, hat, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances
)
results_knn = prequential_evaluation(
drift_stream, knn, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances
)
results_nb = prequential_evaluation(
drift_stream, nb, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances
)
results_autoclass = prequential_evaluation(
drift_stream, autoclass, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances
)
print_summary("HT", results_ht)
print_summary("HAT", results_hat)
print_summary("KNN", results_knn)
print_summary("NB", results_nb)
print_summary("AutoClass", results_autoclass)
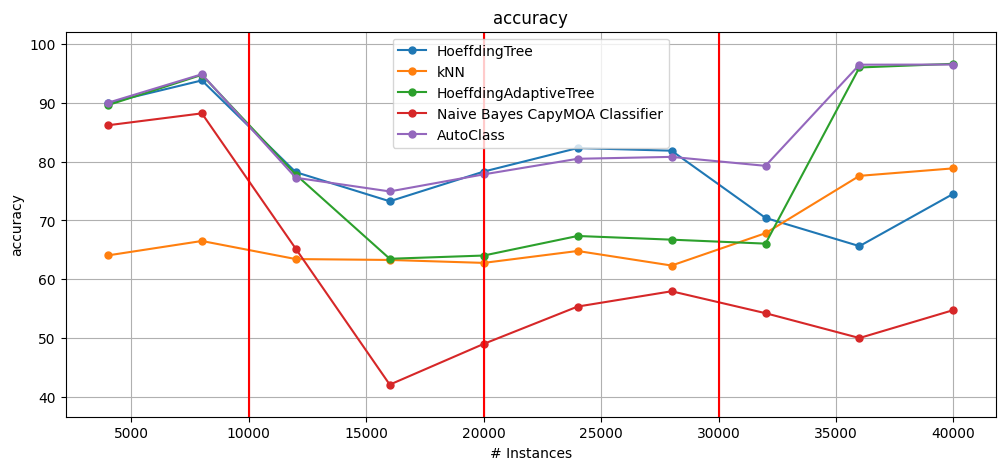
plot_windowed_results(
results_ht,
results_knn,
results_hat,
results_nb,
results_autoclass,
metric="accuracy",
)
HT Cumulative accuracy = 78.82, wall-clock time: 0.326
HAT Cumulative accuracy = 78.24, wall-clock time: 0.364
KNN Cumulative accuracy = 67.14, wall-clock time: 4.948
NB Cumulative accuracy = 60.29, wall-clock time: 0.088
AutoClass Cumulative accuracy = 85.71, wall-clock time: 78.168
9.4 Analysis of further AutoML methods#
Bandit Classifier#
It is a model selection for classification in streaming scenarios.
Each model is associated with an arm. At each train call, the policy decides which arm/model to pull. The reward is the performance of the model on the provided sample. The predict and predict_proba methods use the current best model.
Successive Halving Classifier#
The algorithm progressively eliminates poorly performing models while allocating more resources to promising ones.
Successive halving is a method for performing model selection without having to train each model on all the dataset. At certain points in time (called “rungs”), the worst performing models will be discarded and the best ones will keep competing between each other. The rung values are designed so that at most ‘budget’ model updates will be performed in total.
Testing whether SuccessiveHalvingClassifier and BanditClassifier work correctly#
[10]:
f = io.StringIO()
def test_successive_halving_and_bandit(
stream, max_instances=20000, window_size=2500, budget=None, bandit_eps=0.1
):
"""Test SuccessiveHalving and BanditClassifier for parameter optimization of a single model type."""
print("\n" + "=" * 80)
print("TESTING SUCCESSIVE HALVING AND BANDIT CLASSIFIER FOR PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION")
print("=" * 80)
schema = stream.get_schema()
if budget is None:
budget = max_instances * 2
# Create a wide range of HoeffdingTree configurations with different parameters
ht_models = []
# Test different grace periods
for grace_period in [50, 100, 200, 300, 400]:
# Test different split confidences
for confidence in [0.001, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2]:
# Test different tie thresholds
for tie_threshold in [0.05, 0.1, 0.2]:
ht_models.append(
HoeffdingTree(
schema=schema,
grace_period=grace_period,
confidence=confidence,
tie_threshold=tie_threshold,
)
)
print(f"Created {len(ht_models)} different HoeffdingTree configurations")
# Use SuccessiveHalving to find the best HoeffdingTree configuration
with contextlib.redirect_stdout(f):
shc_ht = SuccessiveHalvingClassifier(
schema=schema,
base_classifiers=ht_models,
budget=budget,
eta=2.0,
min_models=1,
verbose=False,
)
# Use BanditClassifier to find the best HoeffdingTree configuration
bandit_ht = BanditClassifier(
schema=schema,
base_classifiers=ht_models,
metric="accuracy",
policy=EpsilonGreedy(epsilon=bandit_eps, burn_in=150),
verbose=False,
)
# Default HoeffdingTree for comparison
default_ht = HoeffdingTree(schema=schema)
print("\nRunning prequential evaluation...")
results_shc_ht = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=shc_ht,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
results_bandit_ht = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=bandit_ht,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
results_default_ht = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=default_ht,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
# Print results
print("\nEvaluation Results:")
print(
f"[SuccessiveHalving with {len(ht_models)} HT configs] Accuracy = {results_shc_ht.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_shc_ht.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
print(
f"[BanditClassifier with {len(ht_models)} HT configs] Accuracy = {results_bandit_ht.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_bandit_ht.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
print(
f"[Default HoeffdingTree] Accuracy = {results_default_ht.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_default_ht.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
# Calculate improvements
improvement_shc = results_shc_ht.accuracy() - results_default_ht.accuracy()
improvement_bandit = results_bandit_ht.accuracy() - results_default_ht.accuracy()
print("Improvement over default parameters:")
print(f"SuccessiveHalving: {improvement_shc:.2f}% absolute")
print(f"BanditClassifier: {improvement_bandit:.2f}% absolute")
# Plot results
plot_windowed_results(
results_shc_ht, results_bandit_ht, results_default_ht, metric="accuracy"
)
# Display final model info
model_info_shc = shc_ht.get_model_info()
print("\nSuccessive Halving Final Status:")
print(
f"Active models: {model_info_shc['active_models']} / {model_info_shc['total_models']}"
)
print(f"Total rungs: {model_info_shc['current_rung']}")
print(
f"Budget used: {model_info_shc['budget_used']} / {model_info_shc['total_budget']}"
)
[11]:
stream = Electricity()
max_instances = 20000
window_size = 2500
budget = max_instances * 2
test_successive_halving_and_bandit(
stream, max_instances=max_instances, window_size=window_size, budget=budget
)
================================================================================
TESTING SUCCESSIVE HALVING AND BANDIT CLASSIFIER FOR PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION
================================================================================
Created 75 different HoeffdingTree configurations
Running prequential evaluation...
Evaluation Results:
[SuccessiveHalving with 75 HT configs] Accuracy = 87.225, Time: 140.315s
[BanditClassifier with 75 HT configs] Accuracy = 86.145, Time: 81.125s
[Default HoeffdingTree] Accuracy = 85.615, Time: 0.103s
Improvement over default parameters:
SuccessiveHalving: 1.61% absolute
BanditClassifier: 0.53% absolute
Successive Halving Final Status:
Active models: 1 / 75
Total rungs: 7
Budget used: 39999 / 40000
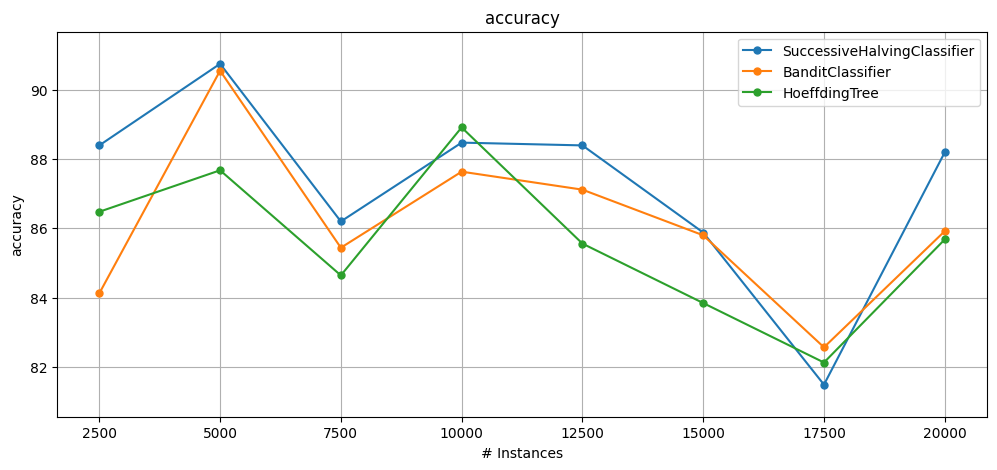
In the initial test, SuccessiveHalvingClassifier delivers the best accuracy (87.2%, +1.6% over HoeffdingTree) but takes 140s, while BanditClassifier is much faster (81s) with similar accuracy to the default, trading precision for speed.
The results highlight a clear accuracy–time trade-off between thorough configuration search and faster, less precise optimization.
9.5 Comparing AutoClass with SuccessiveHalving and BanditClassifier#
[12]:
def base_models_configuration():
# Create base classifiers with same parameters for SuccessiveHalving and BanditClassifier
base_models = []
# Add Hoeffding Trees
for grace_period in [100, 200]:
for confidence in [0.001, 0.01]:
base_models.append(
HoeffdingTree(
schema=schema, grace_period=grace_period, confidence=confidence
)
)
# Add KNN variations
for k in [3, 5]:
base_models.append(KNN(schema=schema, k=k))
# Add Random Forest models
for ensemble_size in [60, 80]:
base_models.append(
AdaptiveRandomForestClassifier(schema=schema, ensemble_size=ensemble_size)
)
# Add Hoeffding Adaptive Trees
for grace_period in [100, 200]:
base_models.append(
HoeffdingAdaptiveTree(schema=schema, grace_period=grace_period)
)
# Add Leveraging Bagging models
for ensemble_size in [60, 80]:
base_models.append(
LeveragingBagging(schema=schema, ensemble_size=ensemble_size)
)
# Add Streaming Random Patches
for ensemble_size in [60, 80]:
base_models.append(
StreamingRandomPatches(schema=schema, ensemble_size=ensemble_size)
)
return base_models
[13]:
def autoclass(stream, max_instances, window_size, budget):
schema = stream.get_schema()
if budget is None:
budget = max_instances * 3
# Initialize AutoClass with the enhanced configuration
autoclass_enhanced = AutoClass(
schema=schema,
configuration_json="./enhanced_autoclass_config.json",
base_classifiers=[
KNN,
HoeffdingTree,
HoeffdingAdaptiveTree,
AdaptiveRandomForestClassifier,
LeveragingBagging,
StreamingRandomPatches,
],
)
results_autoclass_enhanced = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=autoclass_enhanced,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
return results_autoclass_enhanced
def successive_halving(stream, max_instances, window_size):
# Create base classifiers with same parameters for SuccessiveHalving and BanditClassifier
base_models = base_models_configuration()
# Create the SuccessiveHalvingClassifier
with contextlib.redirect_stdout(f):
shc_direct = SuccessiveHalvingClassifier(
schema=schema,
base_classifiers=base_models,
budget=budget,
eta=2.0,
min_models=2,
verbose=True,
)
results_shc = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=shc_direct,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
return shc_direct, results_shc
def bandit_classifier(stream, max_instances, window_size, bandit_eps):
# Create base classifiers with same parameters for SuccessiveHalving and BanditClassifier
base_models = base_models_configuration()
# Create the BanditClassifier
bandit_clf = BanditClassifier(
schema=schema,
base_classifiers=base_models,
metric="accuracy",
policy=EpsilonGreedy(epsilon=bandit_eps, burn_in=150),
verbose=True,
)
results_bandit = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=bandit_clf,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
return bandit_clf, results_bandit
[14]:
def test_autoclass_vs_successive_halving_and_bandit(
stream,
results_autoclass_enhanced,
shc_direct,
results_shc,
bandit_clf,
results_bandit,
max_instances=20000,
window_size=2500,
):
"""Compare AutoClass with enhanced configuration against SuccessiveHalvingClassifier and BanditClassifier."""
print("\n" + "=" * 80)
print("COMPARING AUTOCLASS WITH CONFIG, SUCCESSIVE HALVING, AND BANDIT CLASSIFIER")
print("=" * 80)
# Initialize default models for comparison
print("\nInitializing default models for comparison...")
default_ht = HoeffdingTree(schema=schema)
default_knn = KNN(schema=schema)
default_arf = AdaptiveRandomForestClassifier(schema=schema)
default_hat = HoeffdingAdaptiveTree(schema=schema)
default_lb = LeveragingBagging(schema=schema)
default_srp = StreamingRandomPatches(schema=schema)
# Evaluate default models
print("\nEvaluating default models...")
results_ht = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=default_ht,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
results_knn = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=default_knn,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
results_arf = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=default_arf,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
results_hat = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=default_hat,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
results_lb = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=default_lb,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
results_srp = prequential_evaluation(
stream=stream,
learner=default_srp,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
)
# Print results
print("\nEvaluation Results:")
print(
f"[Enhanced AutoClass] Accuracy = {results_autoclass_enhanced.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_autoclass_enhanced.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
print(
f"[SuccessiveHalving] Accuracy = {results_shc.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_shc.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
print(
f"[BanditClassifier] Accuracy = {results_bandit.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_bandit.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
print(
f"[Default HoeffdingTree] Accuracy = {results_ht.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_ht.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
print(
f"[Default KNN] Accuracy = {results_knn.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_knn.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
print(
f"[Default AdaptiveRandomForest] Accuracy = {results_arf.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_arf.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
print(
f"[Default HoeffdingAdaptiveTree] Accuracy = {results_hat.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_hat.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
print(
f"[Default LeveragingBagging] Accuracy = {results_lb.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_lb.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
print(
f"[Default StreamingRandomPatches] Accuracy = {results_srp.accuracy():.3f}, "
f"Time: {results_srp.wallclock():.3f}s"
)
# Plot results
plot_windowed_results(
results_autoclass_enhanced,
results_shc,
results_bandit,
results_ht,
results_knn,
results_arf,
results_hat,
results_lb,
results_srp,
metric="accuracy",
)
# Display final model info for SuccessiveHalving
model_info_shc = shc_direct.get_model_info()
print("\nSuccessive Halving Final Status:")
print(
f"Active models: {model_info_shc['active_models']} / {model_info_shc['total_models']}"
)
print(f"Total rungs: {model_info_shc['current_rung']}")
print(
f"Budget used: {model_info_shc['budget_used']} / {model_info_shc['total_budget']}"
)
# Display final model info for BanditClassifier
model_info_bandit = bandit_clf.get_model_info()
print("\nBandit Classifier Final Status:")
print(f"Total models: {model_info_bandit['total_models']}")
print(f"Best model accuracy: {model_info_bandit['best_model_accuracy']:.4f}")
print("\nTop performing models:")
print("SuccessiveHalving:")
for i, model_info in enumerate(model_info_shc["top_models"]):
print(
f" {i + 1}. {model_info['model']} - Accuracy: {model_info['accuracy']:.4f}"
)
Test on Electricity Stream#
[15]:
stream = Electricity()
max_instances = 8000
window_size = 2000
budget = max_instances
[16]:
results_autoclass = autoclass(
stream, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances, budget=budget
)
[17]:
shc_direct, results_shc = successive_halving(stream, max_instances, window_size)
[Rung 1] 7 models removed 7 models left 142 instances per model budget used: 1988 budget left: 6012 best accuracy: 95.0704
Top models:
1. StreamingRandomPatches - Accuracy: 95.0704
2. StreamingRandomPatches - Accuracy: 95.0704
3. Leveraging OnlineBagging - Accuracy: 93.6620
[Rung 2] 3 models removed 4 models left 286 instances per model budget used: 3990 budget left: 4010 best accuracy: 88.3178
Top models:
1. StreamingRandomPatches - Accuracy: 88.3178
2. StreamingRandomPatches - Accuracy: 88.3178
3. Leveraging OnlineBagging - Accuracy: 87.3832
[Rung 3] 2 models removed 2 models left 501 instances per model budget used: 5994 budget left: 2006 best accuracy: 90.9580
Top models:
1. StreamingRandomPatches - Accuracy: 90.9580
2. StreamingRandomPatches - Accuracy: 90.6351
[18]:
bandit_clf, results_bandit = bandit_classifier(
stream, max_instances, window_size, bandit_eps=0.3
)
Using 14 provided base classifiers
Chosen model: Leveraging OnlineBagging
Current accuracy: 73.5537
[19]:
test_autoclass_vs_successive_halving_and_bandit(
stream,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
results_autoclass_enhanced=results_autoclass,
shc_direct=shc_direct,
results_shc=results_shc,
bandit_clf=bandit_clf,
results_bandit=results_bandit,
)
================================================================================
COMPARING AUTOCLASS WITH CONFIG, SUCCESSIVE HALVING, AND BANDIT CLASSIFIER
================================================================================
Initializing default models for comparison...
Evaluating default models...
Evaluation Results:
[Enhanced AutoClass] Accuracy = 91.612, Time: 134.935s
[SuccessiveHalving] Accuracy = 91.300, Time: 86.350s
[BanditClassifier] Accuracy = 82.088, Time: 36.171s
[Default HoeffdingTree] Accuracy = 86.462, Time: 0.036s
[Default KNN] Accuracy = 84.775, Time: 0.624s
[Default AdaptiveRandomForest] Accuracy = 90.112, Time: 16.618s
[Default HoeffdingAdaptiveTree] Accuracy = 87.525, Time: 0.065s
[Default LeveragingBagging] Accuracy = 90.188, Time: 6.593s
[Default StreamingRandomPatches] Accuracy = 91.325, Time: 19.369s
Successive Halving Final Status:
Active models: 2 / 14
Total rungs: 3
Budget used: 5994 / 8000
Bandit Classifier Final Status:
Total models: 14
Best model accuracy: 82.7110
Top performing models:
SuccessiveHalving:
1. StreamingRandomPatches - Accuracy: 91.5125
2. StreamingRandomPatches - Accuracy: 91.4375
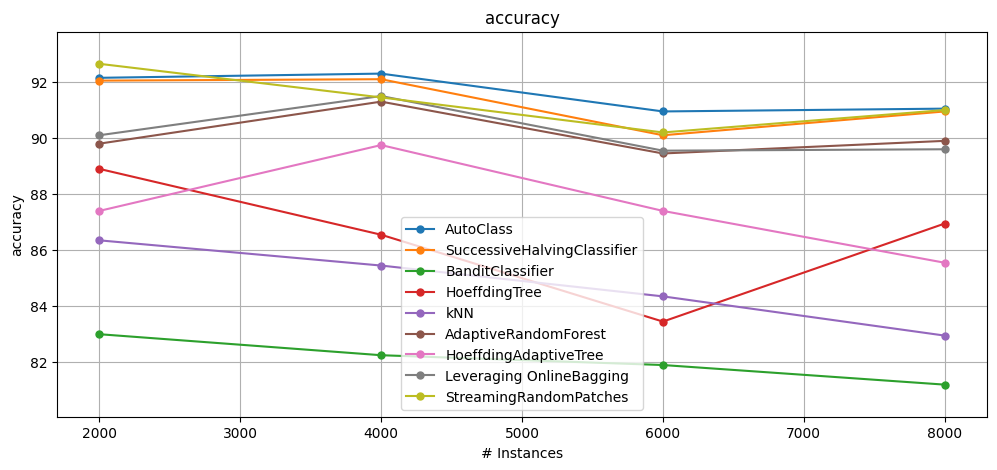
On Electricity, AutoClass achieves the highest accuracy (91.6%) but is slowest (134s).
SuccessiveHalvingClassifier nearly matches it (91.3%) while running faster, offering the best balance.
BanditClassifier (82.1%, 36s) is fastest but underperforms, even below the default HoeffdingTree (86.5%).
Overall, thorough model selection proves more effective here, with SuccessiveHalving striking the optimal trade-off.
Test on custom stream with drift#
[20]:
window_size = 500
max_instances = 8000
budget = max_instances * 3
drift_stream = DriftStream(
stream=[
SEA(function=1),
AbruptDrift(position=3000),
SEA(function=3),
GradualDrift(position=6000, width=2000),
SEA(function=1),
]
)
[21]:
results_autoclass = autoclass(
drift_stream, window_size=window_size, max_instances=max_instances, budget=budget
)
[22]:
shc_direct, results_shc = successive_halving(drift_stream, max_instances, window_size)
[Rung 1] 7 models removed 7 models left 428 instances per model budget used: 5992 budget left: 18008 best accuracy: 80.8411
Top models:
1. HoeffdingAdaptiveTree - Accuracy: 80.8411
2. HoeffdingAdaptiveTree - Accuracy: 80.8411
3. kNN - Accuracy: 80.3738
[Rung 2] 3 models removed 4 models left 857 instances per model budget used: 11991 budget left: 12009 best accuracy: 85.9922
Top models:
1. AdaptiveRandomForest - Accuracy: 85.9922
2. kNN - Accuracy: 84.8249
3. HoeffdingTree - Accuracy: 84.5914
[Rung 3] 2 models removed 2 models left 1501 instances per model budget used: 17995 budget left: 6005 best accuracy: 87.2936
Top models:
1. AdaptiveRandomForest - Accuracy: 87.2936
2. Leveraging OnlineBagging - Accuracy: 85.9296
[23]:
bandit_clf, results_bandit = bandit_classifier(
drift_stream, max_instances, window_size, bandit_eps=0.3
)
Using 14 provided base classifiers
Chosen model: kNN
Current accuracy: 85.1274
[24]:
test_autoclass_vs_successive_halving_and_bandit(
drift_stream,
window_size=window_size,
max_instances=max_instances,
results_autoclass_enhanced=results_autoclass,
shc_direct=shc_direct,
results_shc=results_shc,
bandit_clf=bandit_clf,
results_bandit=results_bandit,
)
================================================================================
COMPARING AUTOCLASS WITH CONFIG, SUCCESSIVE HALVING, AND BANDIT CLASSIFIER
================================================================================
Initializing default models for comparison...
Evaluating default models...
Evaluation Results:
[Enhanced AutoClass] Accuracy = 86.925, Time: 68.542s
[SuccessiveHalving] Accuracy = 86.662, Time: 90.787s
[BanditClassifier] Accuracy = 85.200, Time: 37.273s
[Default HoeffdingTree] Accuracy = 85.100, Time: 0.011s
[Default KNN] Accuracy = 84.275, Time: 0.361s
[Default AdaptiveRandomForest] Accuracy = 86.725, Time: 6.451s
[Default HoeffdingAdaptiveTree] Accuracy = 84.638, Time: 0.020s
[Default LeveragingBagging] Accuracy = 86.450, Time: 2.232s
[Default StreamingRandomPatches] Accuracy = 86.612, Time: 6.846s
Successive Halving Final Status:
Active models: 2 / 14
Total rungs: 3
Budget used: 17995 / 24000
Bandit Classifier Final Status:
Total models: 14
Best model accuracy: 85.0703
Top performing models:
SuccessiveHalving:
1. AdaptiveRandomForest - Accuracy: 86.7625
2. Leveraging OnlineBagging - Accuracy: 86.5125
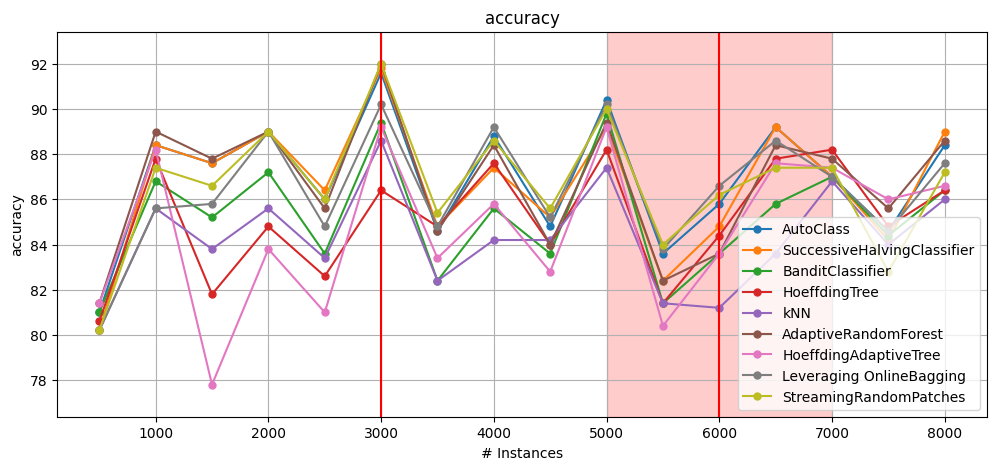
On the drift stream, Enhanced AutoClass reaches the top accuracy (86.9%) with moderate runtime (68s). BanditClassifier (85.2%, 37s) offers the best efficiency-accuracy balance, being more than 2x faster than SuccessiveHalving while losing only 1.4% accuracy.
AdaptiveRandomForest (86.7%) confirms that strong default ensembles can rival AutoML methods.
Overall Analysis#
Across tested streams, the three model selection approaches show consistent accuracy–efficiency trade-offs:
AutoClass: highest (or near-highest) accuracy, especially under concept drift, but slower than BanditClassifier.
SuccessiveHalvingClassifier: accuracy almost the one of AutoClass, but faster.
BanditClassifier: fastest but less accurate.
Guidelines based on these results:
Max accuracy & high resources → AutoClass.
Balance accuracy/efficiency → SuccessiveHalvingClassifier.
Time/resource-constrained → BanditClassifier.